Curiosities, construction and design of wind turbine blades
How do wind turbines work?
Wind turbines blades produce electricity by harnessing the natural energy of the wind to drive a generator. Wind is a clean, sustainable source of energy that never runs out, and the transformation of its kinetic energy into electrical energy produces no emissions.
Wind turbines blades are the natural evolution of windmills and today are high-tech devices. Most turbines blades generate electricity as soon as the wind reaches a speed of between 3 and 4 meters per second, generate a maximum power of 15 meters per second and are disconnected to prevent damage when there are storms with winds blowing at average speeds of over 25 meters per second during a temporary interval of 10 minutes.

Why are three-bladed wind turbines the most commonly used?
Why do wind turbines blades always face the same direction?

Types of wind turbines
Horizontal axis wind turbines with blades
Most common in wind farms. Their axis of rotation is oriented parallel to the ground, and they have a high hub height. In addition, they incorporate a rotor mechanism that allows the wind turbine to be oriented according to changes in wind direction.
Most horizontal axis models use three blades, making them the most efficient option due to their optimal balance between stability and performance.
Vertical-axis wind turbines with blades
In these wind turbines, the axis of rotation is perpendicular to the ground, which eliminates the need to orient them towards the wind. Another advantage is that they do not require a considerable height to harness their power. However, they are less efficient than horizontal axis wind turbines.
Characteristics of a wind turbine
Multiplication effect
The rotor (a set of three blades mounted on the hub) turns a slow shaft connected to a gearbox that increases the rotational speed from about 13 to about 1,500 revolutions per minute.
Automatic guidance
Generation of power
The gearbox, through the fast shaft, transfers its energy to the coupled generator, which produces electricity.
Blade rotation speed
The wind rotates the blades, which start to move at wind speeds of about 3.5 m/s and provide maximum power at about 11 m/s. In very strong winds (25 m/s) the blades are placed in flag and the wind turbine is slowed down to avoid excessive stresses.
Evacuation of the power
The energy generated is conducted inside the tower to the base and, from there, through a subway line to the substation, where its voltage is raised to inject it into the electrical grid and distribute it to the consumption points.
Monitoring of the system
All critical wind turbine blades functions are monitored and supervised from the substation and the control center to detect and resolve any incident.
What material is used to make wind turbine blades?
The blades of a wind turbine are made of three materials that allow to support the large structure adapted to a balance between lightness and resistance.
- Fiberglass: provides structural strength, is light and also flexible, allowing it to withstand the stress caused by gusts.
- Carbon fiber: it is light, resistant and provides durability and allows complex shapes to be modeled.
- Polyester or epoxy: reinforces the fibers, guaranteeing the blades’ resistance to fatigue and environmental wear.
Other wind turbines FAQ’s and curiosities
Some of the most frequently asked questions around wind turbine blade design and wind farms are the following.
How does the wind move the blades?
How does the tower support so much weight?
Wind turbine blade material
How is maintenance carried out?
How are blades repaired?
How do you decide where to install a wind farm?

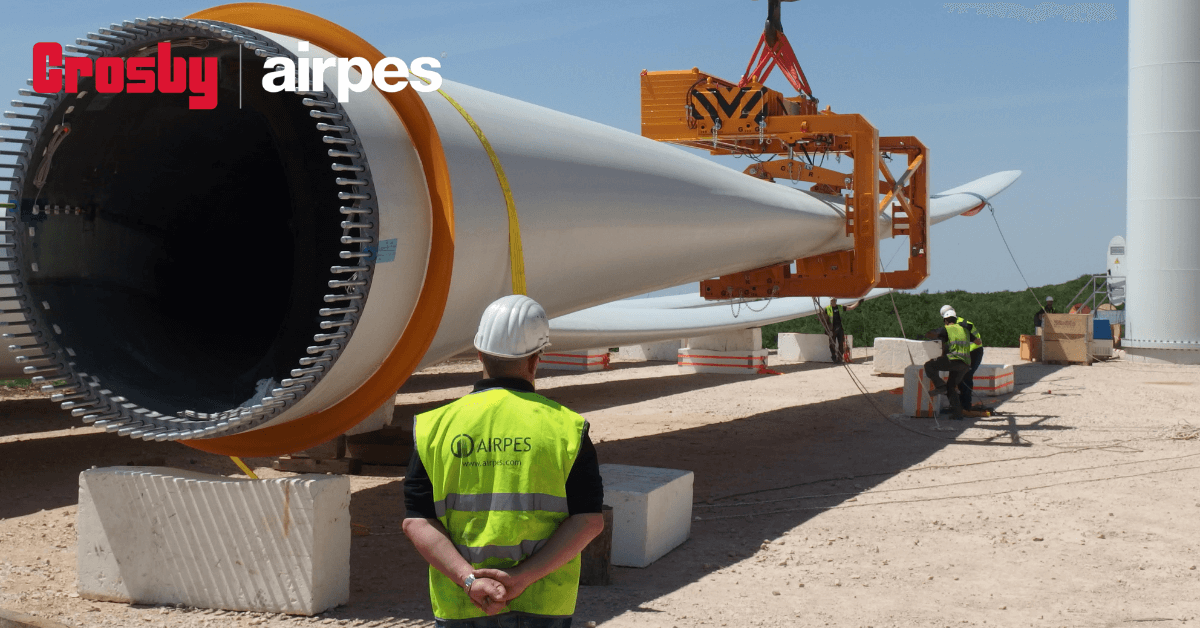
Solutions for transport and handling wind turbine blades
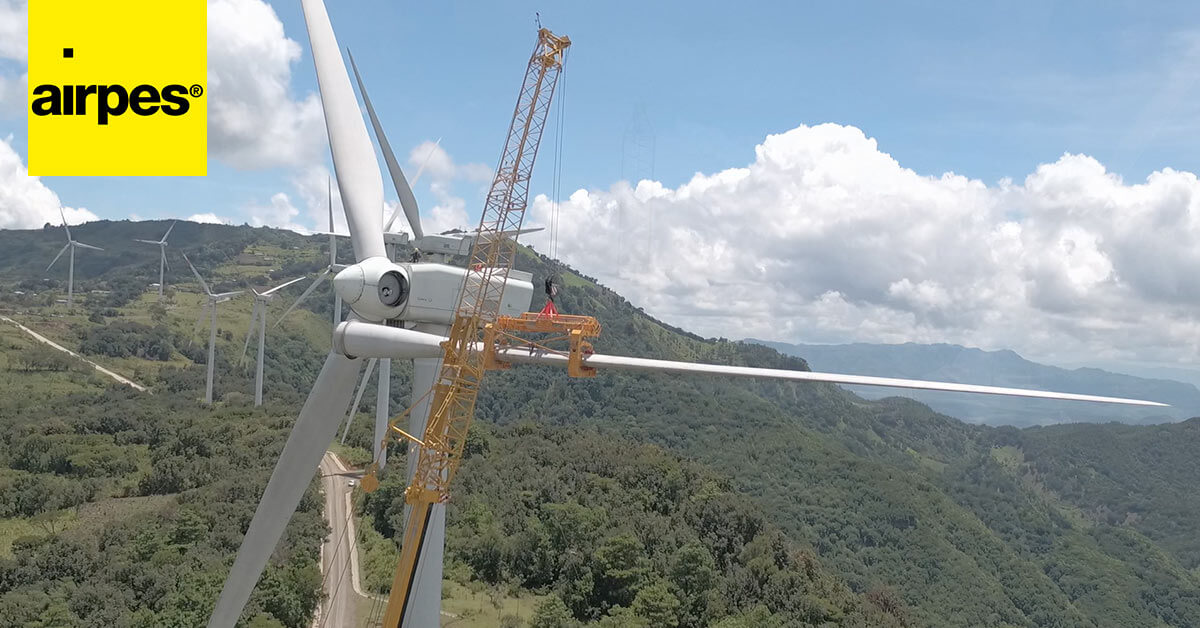
Transporting and assembling wind turbine blades that exceed 80 meters in length is a major logistical challenge. To carry out wind farm installations, it is essential to have the equipment and tools that fit your project’s needs.
To make time efficient of transport, assembly and installation of wind turbine blades can be used the following tools:
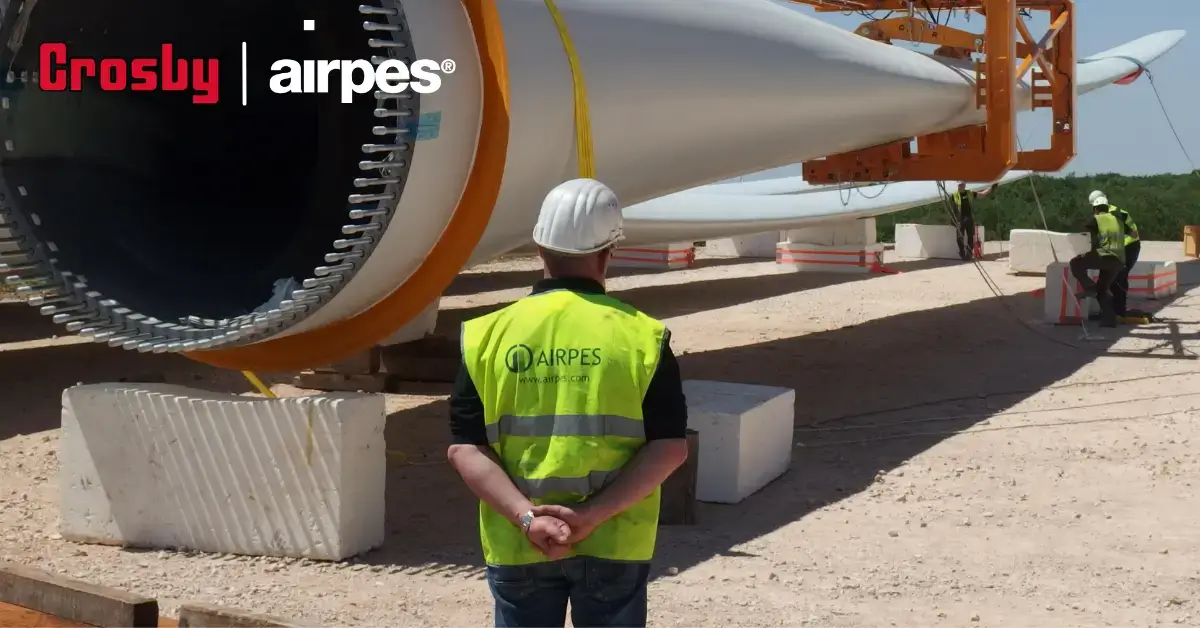
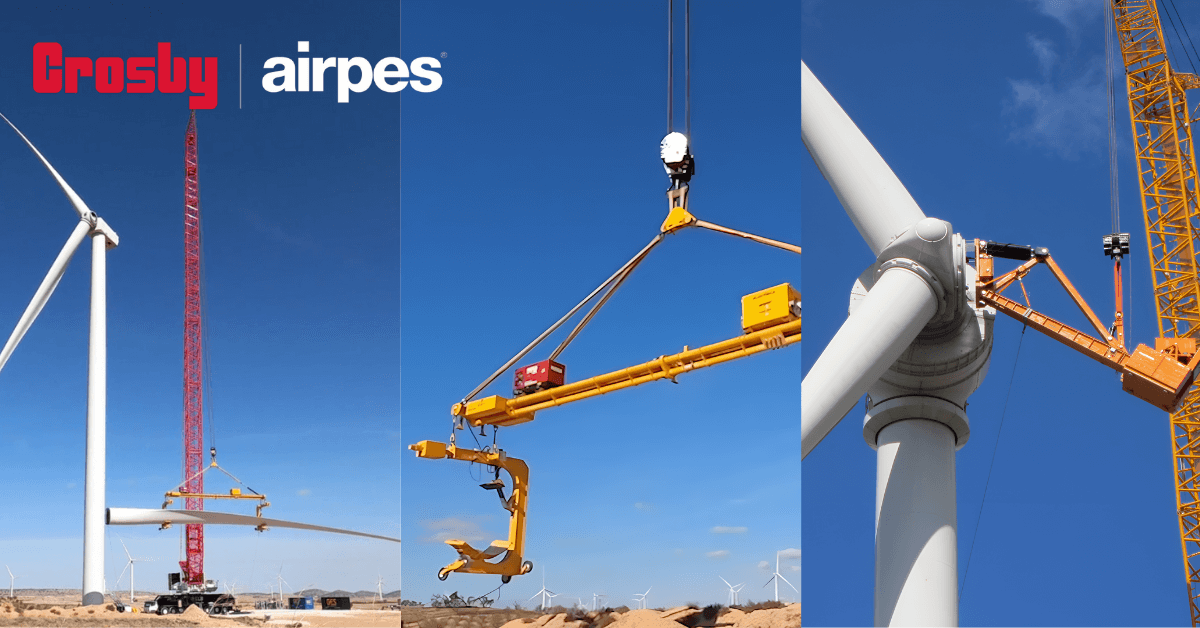
Blade Transport Tool
It is a tool designed for safe loading and unloading of wind turbine blades in manufacturing plants.
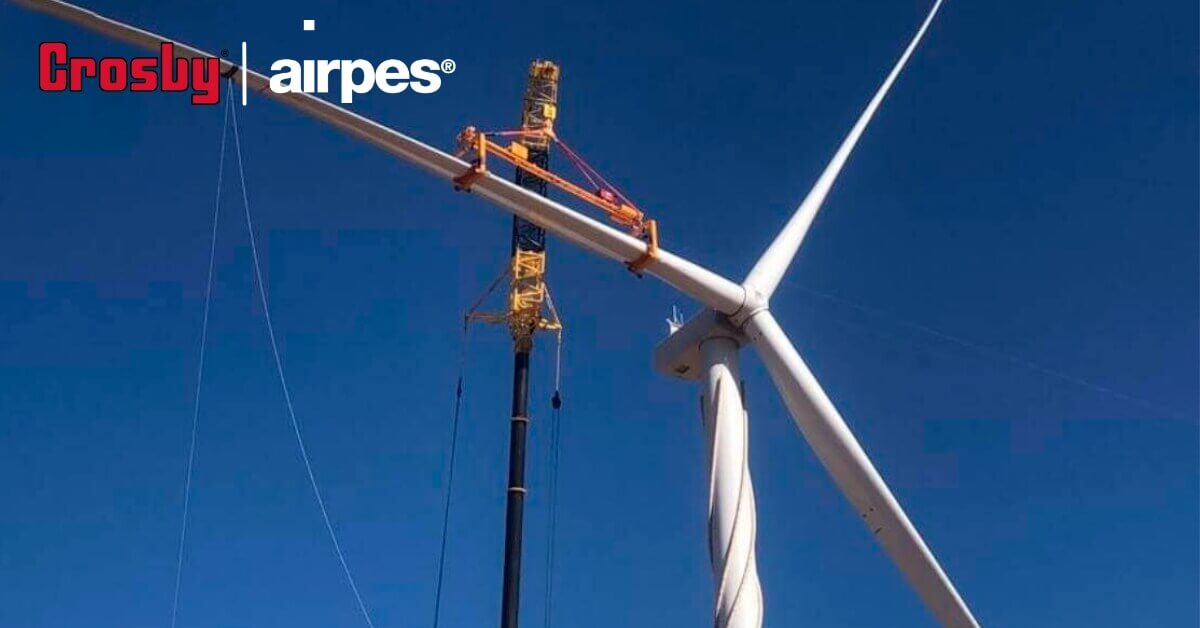
Lifting system
Custom-designed solution for lifting and handling wind turbine blades during transport, maintenance or installation to minimize the risk of structural damage.
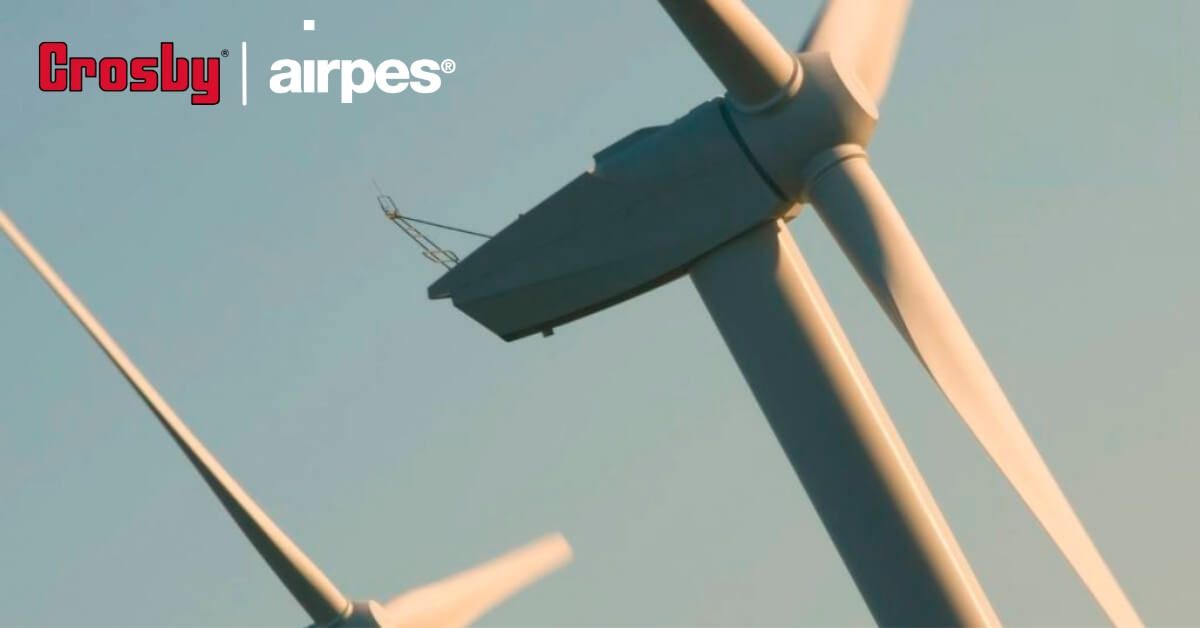
Crane-less blade exchange system
Solution that allows the replacement or exchange of wind turbine blades without the need for cranes, in remote locations or difficult access where the use of cranes would be logistically complex or costly. It also allows to guarantee an agile, sustainable operation, reducing costs.
We design projects to suit the specific needs of a wide range of companies and industries Explore our transportation tools

Boost your wind energy projects
We are supplier of equipment for wind farm installation and maintenance. We offer solutions tailored to your needs and provide advice throughout the entire process of designing and manufacturing tools for lifting, installation and transportation tasks in the wind industry.






